Driving question: What is the perfect length of a paper football field? We are talking, one that allows some paper footballs to score goals, but not every “kick.”

Goal: Students will create and use a line plot to categorize data in a way that makes it easy to interpret. They will analyze the data to determine the best measurement for flicking a paper football accurately.
Prep: I folded a paper football out of an ordinary,letter-sized piece of paper (8 ½ by 11 inches). You fold it the same way you fold an American Flag. Have one pre-folded, but this could be part of the lesson, if you have time. (I didn’t have X.)
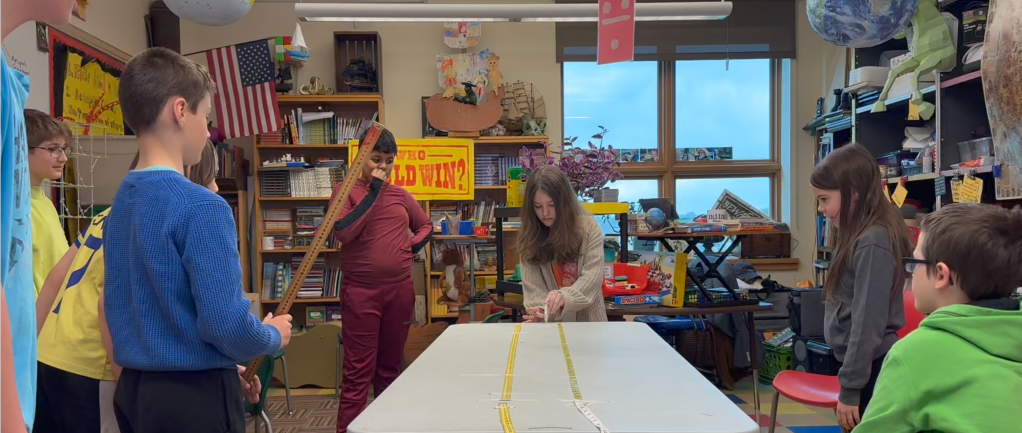
I placed two tables end to end, creating a lengthy runway for measuring. Before students arrived, I taped rulers to the table top the entire length of the two tables, about 3 inches away from the center. I put pieces of tape at each foot so that it would be faster and easier to locate the increment.
Lesson: I told the students the object of the lesson was to determine the “goldilocks length” of a paper football field for this group of students. Another group may be better or worse at flicking the paper football. We are going to collect data that will help us tailor our “field” to our group.
“We don’t want the field goal too close, or every single flick will score a point. We also don’t want the field goal too far away. Then no one will score! There will be a window where some will score, but some won’t. We will use data to find that sweet spot. And, we will use a line plot to help us read the data.”

The first thing we did was figure out the width of the field goal, so that we could finish constructing our mock field. I had each student form right angles with their thumbs and index fingers. Then, touching thumb-tips, they placed their finger field goals on the measuring tape (ruler) I had already taped to the tables. As students shared the measurements of their finger field goals, I wrote them on the dry erase board. We had 6, 6, 5, 5 inches.
I had taught my students how to average numbers earlier in the year. They were bouncing with the information, now. “It’s 5.5,” a girl offered.
“How do you know?” I queried.
A boy suggested that it was right in the middle of the numbers. I affirmed this by circling the middle four and five. The girl who had provided the original answer shared what she did to get it, and what one should do to find the average of several numbers. “You add all of the numbers, and then divide by the number of numbers.” We discussed dividing 22 by four in order to review fractions and decimals, and to double-check our answer.
Next, we used mini (six inch) rulers to measure five and a half inches distance between the already taped down ruler and a new one. I had the students tape it down. Now, we had a runway that was the average field goal width, running about ten feet long.
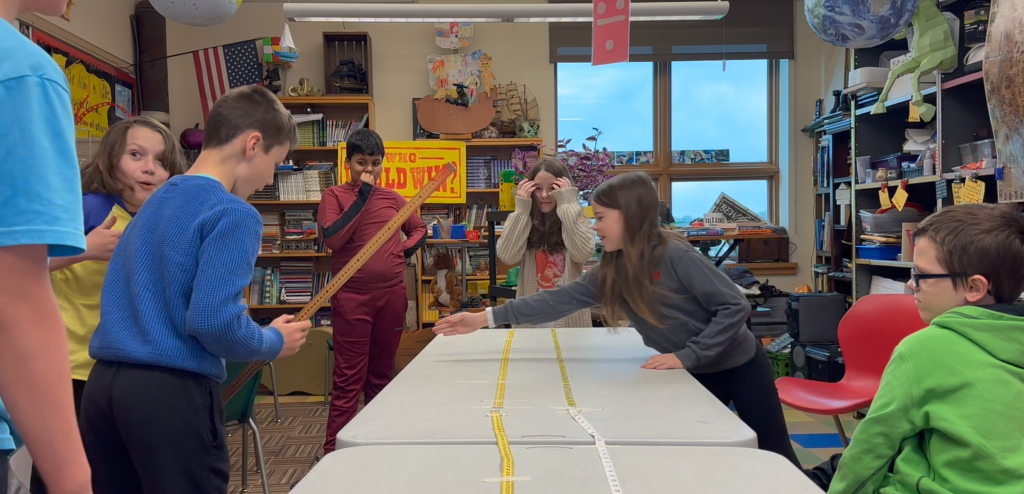
I demonstrated how to flick the paper football. Each student got three tries. If any of them were duds (didn’t fly), we conducted a retry. There were a few very short flicks, but all in all we collected some valuable data.

About half of the flicks landed between the two rulers; within the field goal range. These measurements were written on the board in one color. The flicks that did not land between the rulers were recorded in a different color. All of the measurements were recorded to the nearest ⅓ of a foot, in order to use mixed numbers on our line plot.



Once the line plot was finished, it was easy to see the window where the field goal ought to be erected. There was a collection of accurately-flicked colored Xs up to a point. Then the other color, the color of missed flicks began to move in. At a certain point there were no longer any accurate flicks. The brackish space containing both colors contained the available distances.
Some students wanted to place the field goal at the first measurement that recorded a miss. I explained that, were we to place it there, nearly every flick would score a point. Even the misses that went far could pass between the goal posts before veering off to the side. I drew a picture illustrating what I meant.
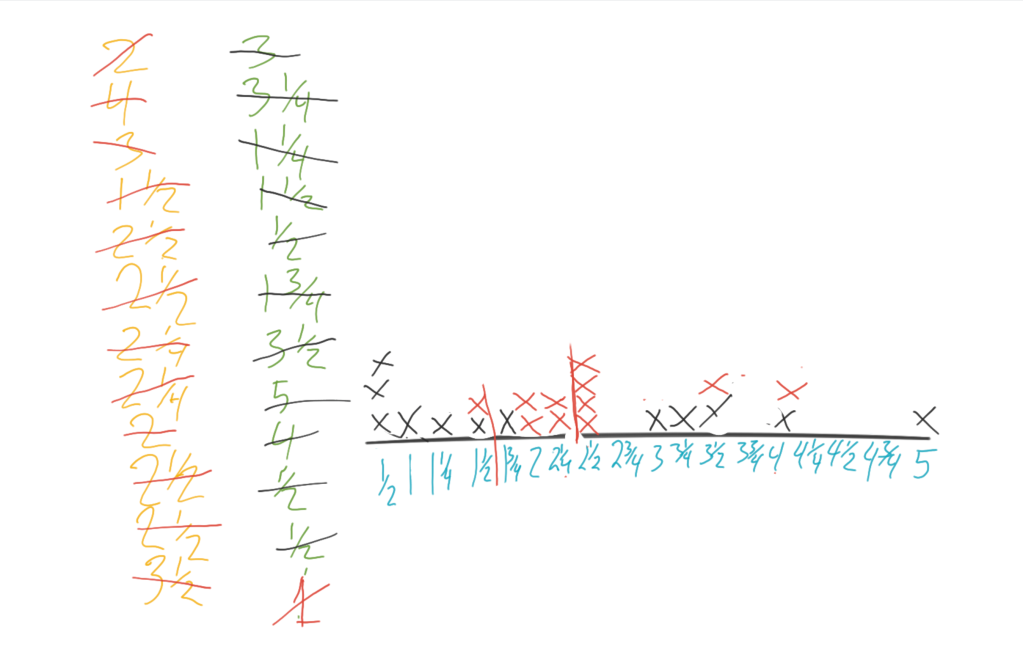
One student wanted the goal posts erected right before the very last successful data point; The last one to land between the two rulers. I told him that “This would guarantee that only one person would get one point for one flick out of… How many did we do? That might be too frustrating, and not very fun.”
We ended the lesson without deciding on the perfect distance. Basically, the thing to do was to use the data that we collected to try out some reasonable distances, and see which ones were more fun. The beauty of the paper football field goal game is that the field is so malleable. It is all about fun, and that’s what I hoped the line plot lesson would generate. If nothing else, it was memorable.
