“How many more squares is White attacking than Black?”
This problem was awesome on a few fronts. Students had deciphered a Morse code message that shared a short sequence of chess moves written in algebraic notation. They played out those moves and discovered that one player had a huge advantage over the other. “How much of an advantage? Be specific. Can you put a numeric value to the advantage?”
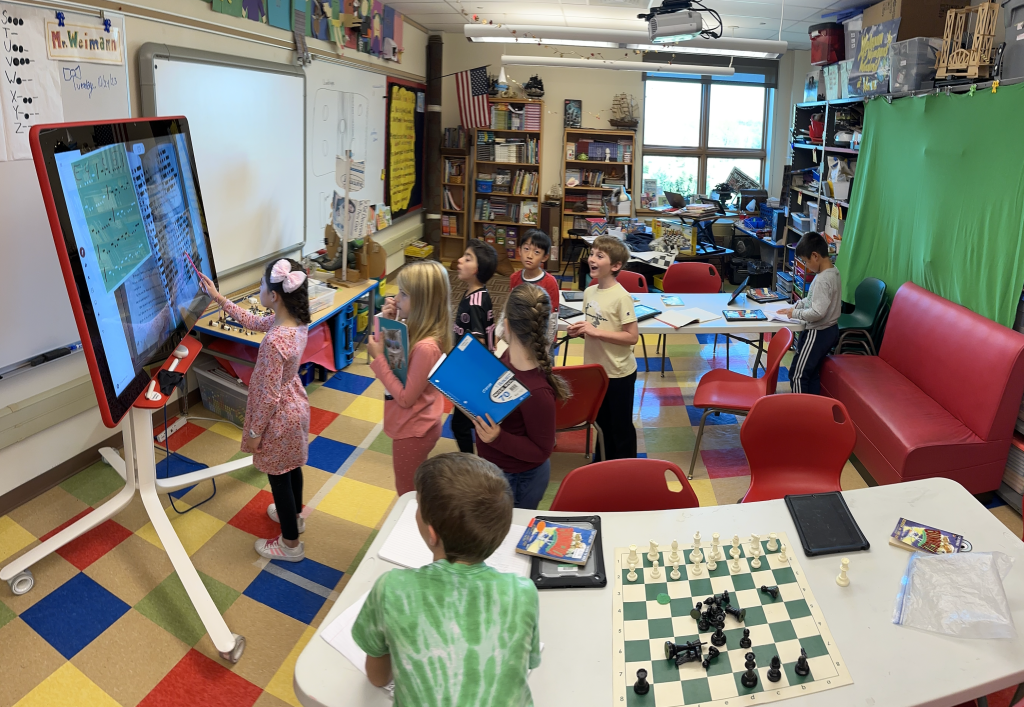
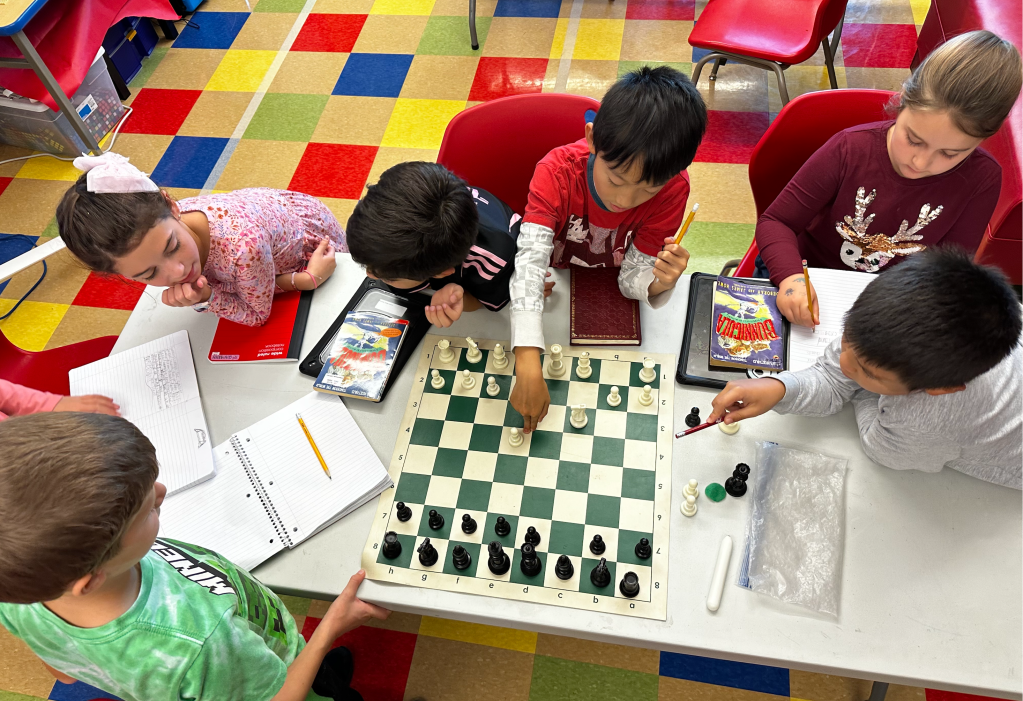








It all began with my preparing a lesson for chess club. I was going to teach club members about gambits. I researched the more common gambits and landed on the Smith Morra Gambit. I found a succinct video on Youtube that explained the gambit. While watching the video, I wrote down the algebraic notation.
But, I wouldn’t just give them the chess code to learn the gambit; I decided to have my gifted students decode the code! My fifth grade gifted students were the first ones to see the code. They had only dabbled with decoding Morse messages.

I had used Morse Code Translator to change the chess play sequence into dots and dashes. Rather than writing the number of the move; This was going to be confusing enough as it was; I decided to change the colors of the moves. White’s moves were turned to white dashes and dots. I made the background of the text box green, so that you could easily see the white and black codes. I put an image of my code, along with the Morse Code alphabet and accompanying numbers onto a Google Jamboard. The fifth grade gifted students were on it the moment they walked through the door.





The two things that I shared with the fifth graders was that the slanted line (/) separates the words; In this case it broke up the moves, but I did not explain that. I told them nothing about the actual message. The second thing that I pointed out was where each letter or number’s code ended. The translator that I use makes it much easier and faster to produce Morse Code, but sometimes it is difficult to locate the space between each letter/number. After pointing out these two key factors, I stepped back and watched the struggle.
Right away I heard a couple students divvy up the White and Black “words.” I was glad to hear the idea of collaboration. I wondered how long it would take for someone to understand that these were not actually words. The very first coded move was e4, the most popular opening move in all of chess. I heard a few people verbalize bafflement, but several recognized the move, “It’s chess!” someone shouted.


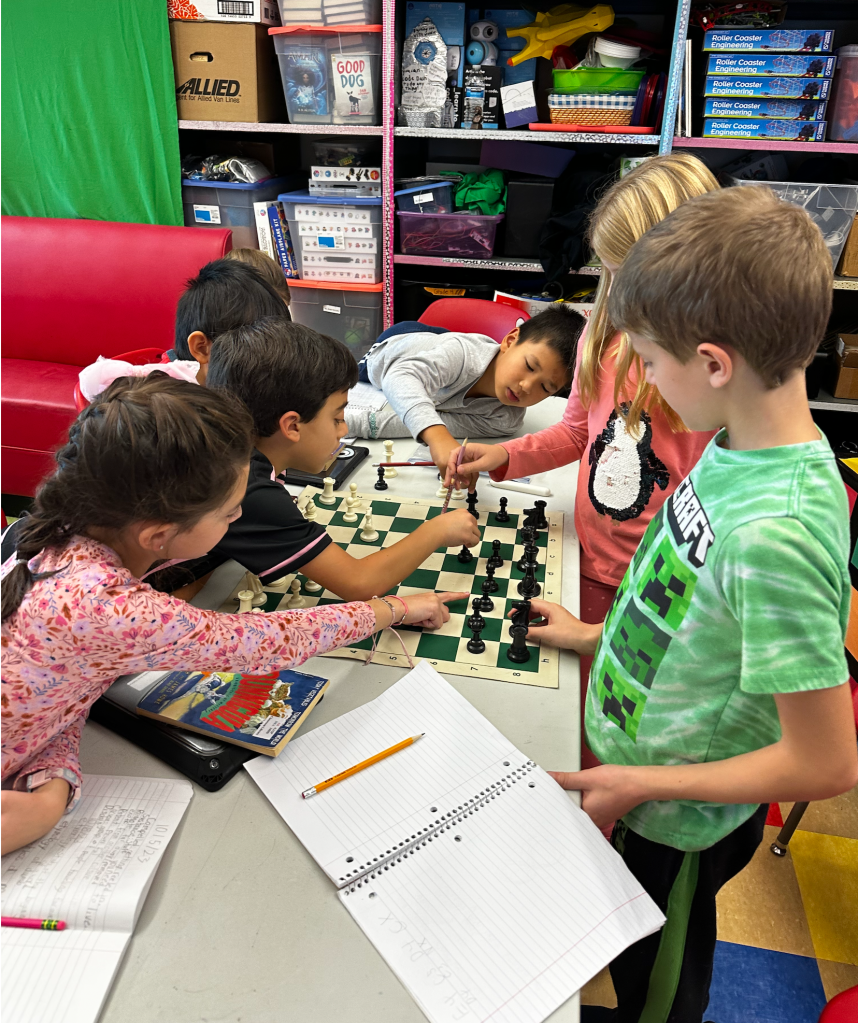
I didn’t help them with any of it. At least one student knew enough to be able to read most of the algebraic notation and make sense of the moves. Of course I had a chess board and pieces handy, and we set up a game. I let the students figure out the sequence of play. When they came to the gambit on the second White move, I stopped them to explain what a gambit was. This was good practice for my chess club lesson that afternoon. A couple kids would get a double lesson, but that was okay. They could be my co-teachers!
“The word gambit is closely related to gamble. It means taking a risk. A chess gambit happens when one player offers up a peace as a sacrifice in order to draw an opponent into a trap or sequence of moves that would benefit the aggressor (the one offering the gambit). Do you capture the sacrifice or risk the piece taking your own?”
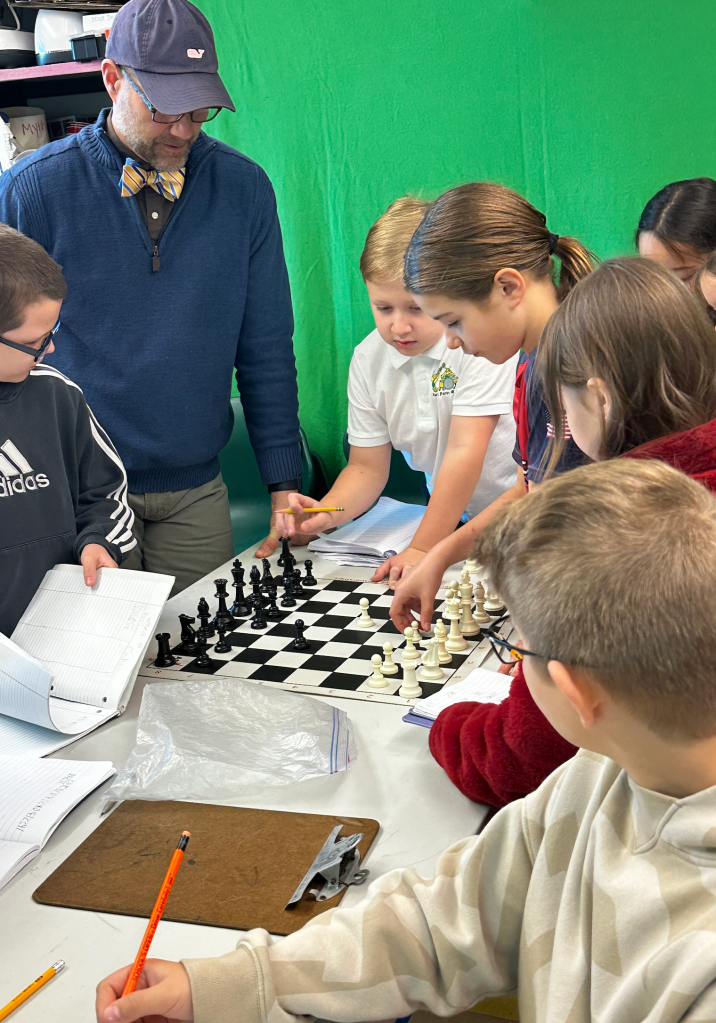







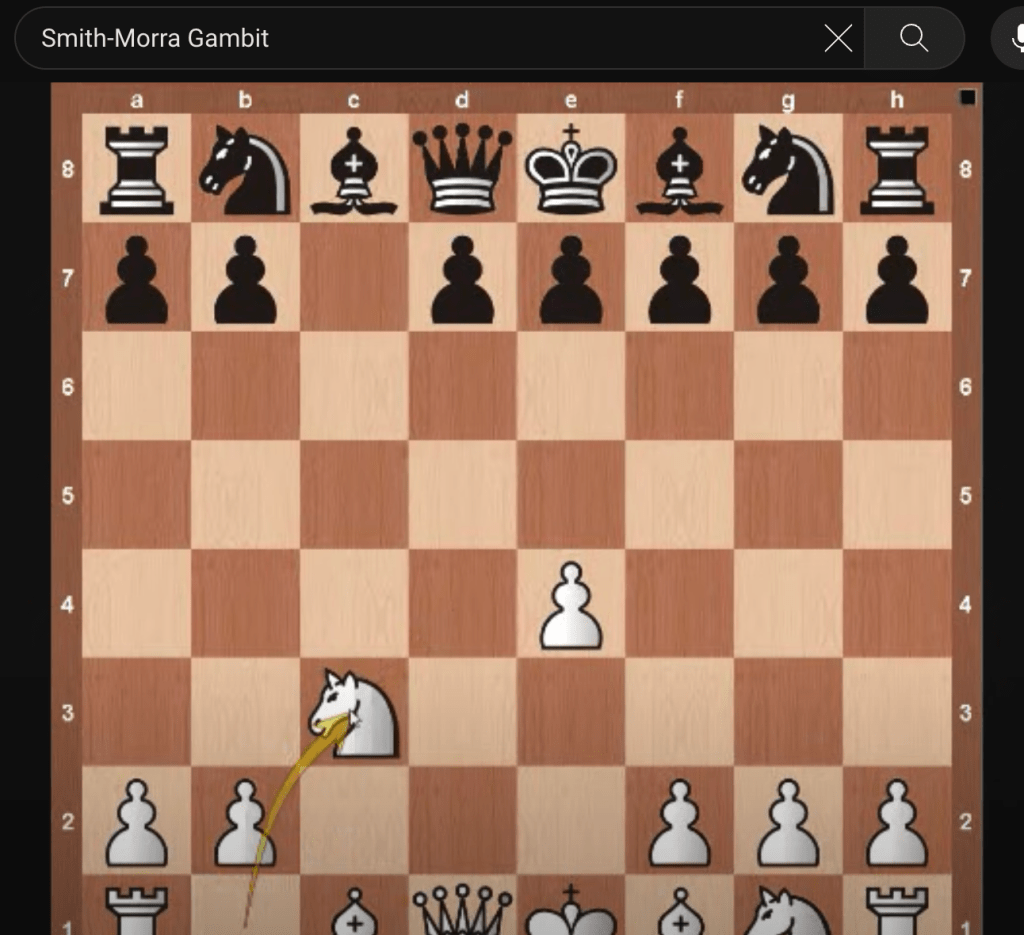
I had the fifth graders play through the short sequence until Black’s pawn was captured. Black had accepted the gambit, capturing the initial White pawn placed on d4. White offered up another pawn on c3. When Black captured that, White might feel a little on edge, because now there is a Black piece threatening the second rank of the White team! It is so close to attacking the Queen!!
Before any more damage can be done, White captures with the Queen-side Knight, Nxc3. White has lost two pawns, while Black is only down one. If you were to only count points, it would appear that Black has the advantage, being up a point. A mere glance at the board should show even a novice player that White is in a much better position!
I explained to the fifth grade gifted students that the best thing to do at the beginning of a game of chess is to control the middle of the board. With that criteria, everyone can easily see the trap that Black has fallen into. There is a White pawn left sitting on the initial e4 square. And, now a Knight is “developed,” backing up the e4 pawn and attacking four more squares (b5 and d5 as well as a4 and e2).
The fifth grade lesson stopped there, but my fourth grade gifted students got a treat. It only took seconds for them to figure out that the Morse Code message was algebraic notation for a chess game. When I heard some groans, I told them, “The first to solve the riddle can play me in a game of chess.” Now, the heat was on. I set the board back up in the middle of a table while my students grappled over letters and numbers seemingly unrelated to one another.
We worked through the Smith Morra Gambit sequence the same way I had with fifth graders. I had the fourth graders figure out the algebraic messaging. They figured out that the Xs meant a piece had been captured. I had to explain that the “d” in dxc3 meant that the capturing pawn had come from the d file. After explaining gambits and discussing the advantages and disadvantages of the board we were left with, I played a blitz round of chess against a pair of students.
Third grade was next, and these students are not only classy, but they are some of the hardest workers I’ve witnessed. Their grit knows no end. I presented them with the same problem. They labored through decoding my Morse Code message. We played the sequence out. I taught them what a gambit was, and we discovered the significant advantage that White was left with. But… Then I was hit with a question that I liked so much that I recorded it on video so that I would remember it: “We know that White has the advantage, but how much of an advantage? Can we put a number to it? How many more squares is White attacking than Black?”
Not all of my third graders know how to play chess. I taught the team how each piece attacks. “How many squares is the King attacking?” I asked. I showed them how it moves. The answer was two squares. “How many squares are the Bishops attacking?” We looked at their lines of attack. I showed them the squares that the Queen attacked, including the Black pawn on d7. We went over how a pawn attacks diagonally and the way a Knight moves. Then I set them loose.

A few floundered, so I guided them to make a T chart. “Let’s do one color at a time,” I suggested. “Also, how about we focus on only one piece?” We carefully counted all of the squares that the Black pawns were attacking (12). Then we counted up the Knights’ attacks (4).
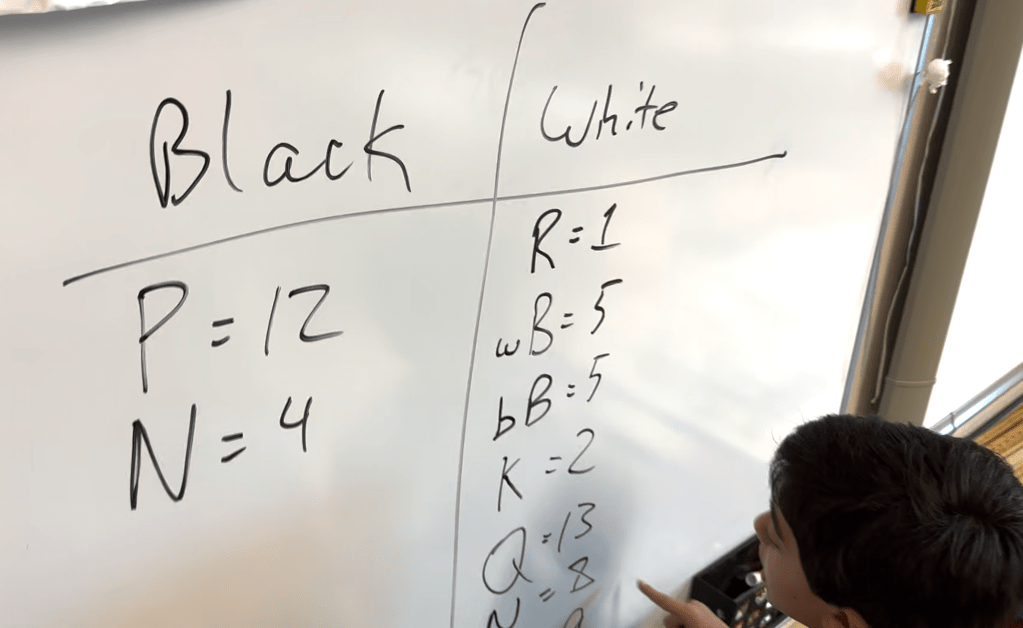
Next we moved on to White. There was an empty square next to the White Rook, so that counted as an attacked square. We continued counting until we covered every piece. I missed a couple of the the Knight’s attacks, but Gray got my back. She caught my mistake, and we corrected the calculation.
In the end, we discovered that White was attacking 43 squares to Black’s 16, way more than twice as many! So, was the gambit worth it? I’d say so. And, what could Black do differently to limit the massive advantage? Don’t fall for it. Don’t take the gambit. Push forward or ignore, but definitely think ahead.
